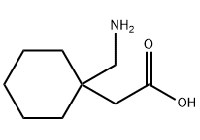
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given gabapentin for diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia have a meaningful benefit.
Gabapentin, like other gabapentinoid drugs, acts by decreasing activity of the α2δ-1 protein, coded by the CACNA2D1 gene, first known as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels. However, see Pharmacodynamics, below. By binding to α2δ-1, gabapentin reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters (primarily glutamate) and as a result, reduces excess excitation of neuronal networks in the spinal cord and brain. Sleepiness and dizziness are the most common side effects. Serious side effects include respiratory depression, and allergic reactions. As with all other antiepileptic drugs approved by the FDA, gabapentin is labeled for an increased risk of suicide. Lower doses are recommended in those with kidney disease.
Gabapentin was first approved for use in the United Kingdom in 1993. It has been available as a generic medication in the United States since 2004. It is the first of several other drugs that are similar in structure and mechanism, called gabapentinoids. In 2023, it was the ninth most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 45 million prescriptions. During the 1990s, Parke-Davis, a subsidiary of Pfizer, used several illegal techniques to encourage physicians in the United States to prescribe gabapentin for unapproved uses. They have paid out millions of dollars to settle lawsuits regarding these activities.
Medical uses
Gabapentin is recommended for use in focal seizures and neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is prescribed off-label in the US and the UK, for example, for the treatment of non-neuropathic pain, anxiety disorders, sleep problems and bipolar disorder. In recent years, gabapentin has seen increased use, particularly in the elderly. There is concern regarding gabapentin’s off-label use due to the lack of strong scientific evidence for its efficacy in multiple conditions, its proven side effects and its potential for misuse and physical/psychological dependency. Some harms, including nervous system harms, have been underreported in published trials of gabapentin, potentially resulting in the underestimation of harms in guidelines for the use of gabapentin.